Using the "if-else" logic in EDC/CDMS
Table of Contents
This tutorial will cover what an if/else statement is, when to use it, and how to use it.
What is an if/else statement
The if/else statement is a logical, conditional expression that evaluates a condition and will only execute the block of code below it, if the condition is true.
An example in plain English:
if (field 1 = 1 and field 2 = 2) {
'Perform this operation';
} otherwise if (field 1 = 1 and field 2 = 1) {
'Perform this operation instead';
} otherwise {
'Perform this operation since both other conditions failed';
}Putting this into JavaScript code, we get the following:
if('{field1}' == 1 && '{field2}' == 2 ){
'This combination is not possible';
} else if('{field1}' == 1 && '{field2}' == 1 ){
'This looks good';
} else {
'This looks fine too';
}In the example below, the calculation field is used to check whether a patient fulfills all inclusion criteria:
if ({pat_has_example} == 1 && {inc_consent} == 1 && {pat_65} == 0){
'Yes';
} else {
'No';
}This is how it looks like in the data entry view:
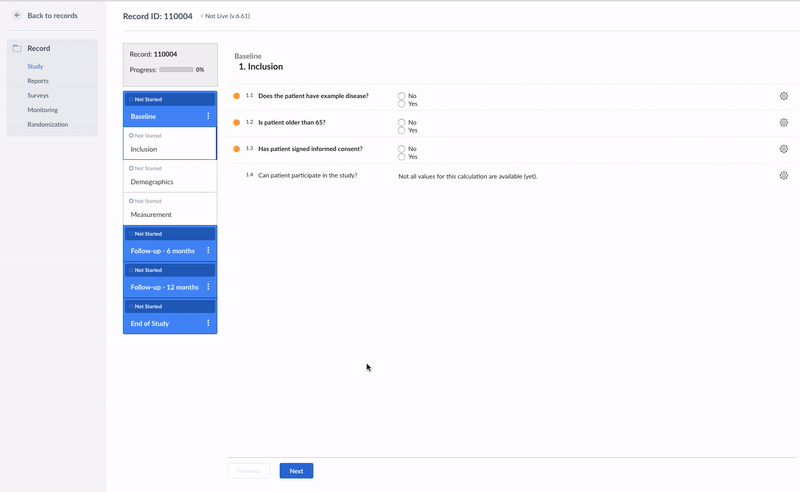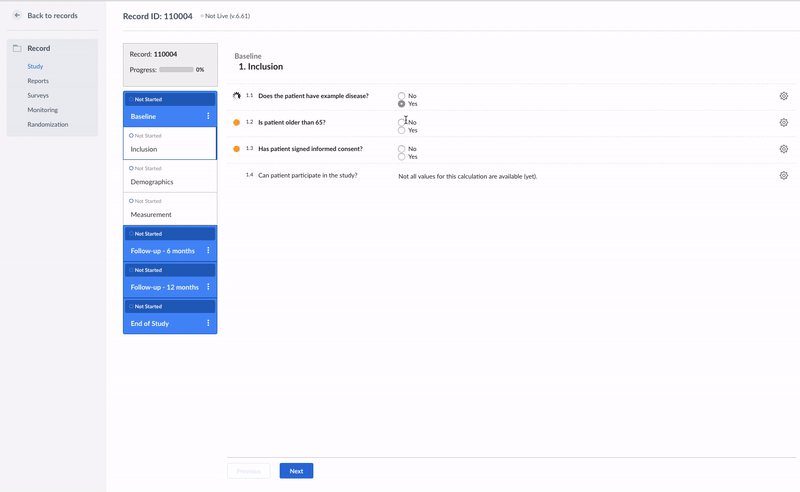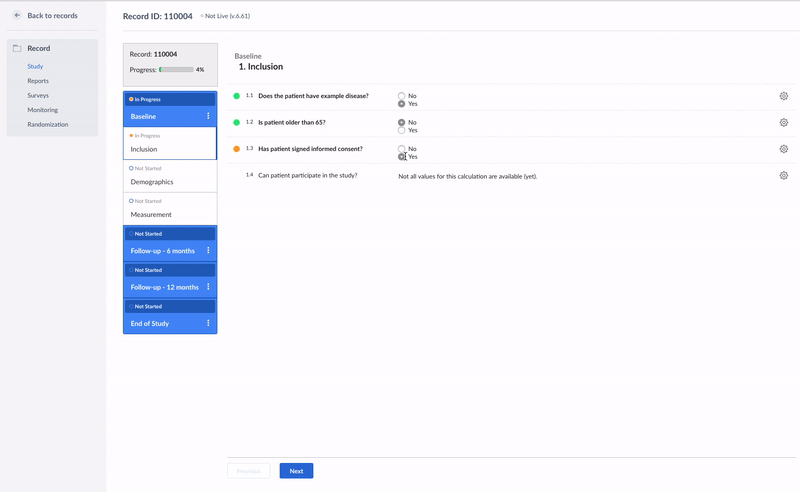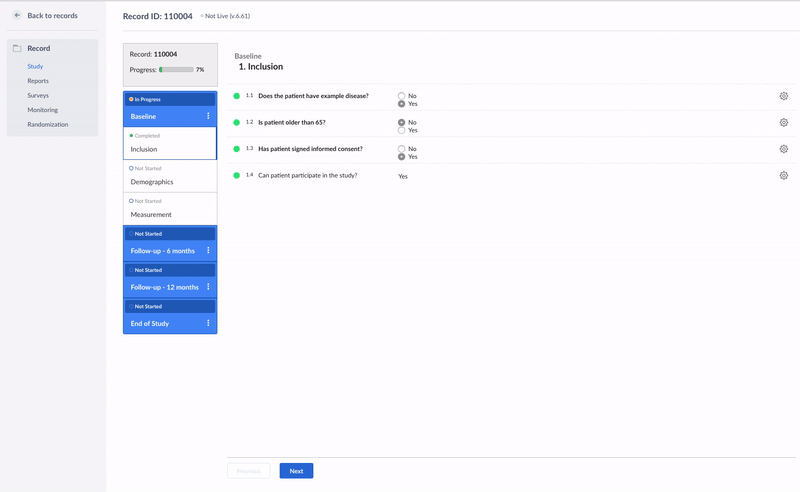
It is possible to combine the statements using two operators:
| Operator | Meaning |
| == | equal to |
| != | not equal to |
| && | and |
| || | or |
| < | less than |
| > | greater than |
| <= | less than or equal to |
| >= | greater than or equal to |
Please note that you have to use two characters as operator.
Read more about JavaScript Operators.
When to use the if/else statement
Use the if/else statement when you want a certain task to be performed only when a condition is met. If you find yourself using "If ... then" statements to describe your calculation workflow, you should use this conditional expression.
For example: If a patient is female and is pregnant, then I want to calculate the expected due date in days.
Translated into JavaScript:
if ('{gender}' == 'female' && '{pregnant}' == 'yes') {
due_date = 280 - {days_pregnant};
} else if ('{gender}' == 'female') {
'Not pregnant';
} else {
'Male subject';
}Notice that the second condition (else if gender is 'female') is automatically true if the first statement is true. That's okay! The program will stop as soon as it meets the first statement that evaluates to true. You can check the example above in the calculation helper.
You can get more examples of if/else statements on Castor Form Exchange.
Using several if/else statements
In some cases, when it is necessary to evaluate several conditions, it it necessary to use several ELSE-IF statements after each other. There is no limitation to the number of consecutive statements.
The example below uses several 'else...if' statements to calculate a score based on the patient's age.
Depending on the age, certain score applies:
var age = {patient_age};
var score = 0;
if (age < 18) {
'Patient cannot participate in te study';
} else if (age >= 18 && age <= 30) {
score += 3;
} else if (age >= 31 && age <= 50) {
score += 5;
} else if (age >= 51 && age <= 65) {
score += 7;
} else {
score += 1;
}
score;
Check the example below in the calculation helper.